Leptospirosis Diagnosis of Punjab CM Bhagwant Mann
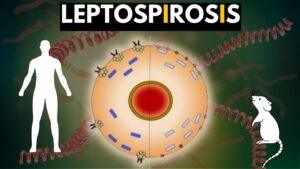
Punjab Chief Minister Bhagwant Mann has been diagnosed with leptospirosis, a bacterial infection often transmitted through contact with the urine of infected animals, such as rodents or dogs. He was admitted to Fortis Hospital in Mohali with symptoms, including pulmonary artery inflammation. Doctors confirmed his diagnosis through blood tests and initiated antibiotic treatment. Mann is currently stable and showing significant improvement in his clinical parameters. Leptospirosis is typically contracted in tropical regions and can lead to serious health complications if untreated.
Leptospirosis and Its Transmission

Leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans. It is most prevalent in warm, humid environments where the bacteria can thrive. The bacteria typically enter the human body through skin abrasions, mucous membranes, or the eyes, nose, and mouth. In most cases, people contract the infection through activities that involve contact with contaminated water or soil, such as swimming in lakes, farming, or working in environments where animal waste is present. The disease is particularly prevalent in areas prone to flooding, where the risk of contamination increases due to the spread of animal waste in water bodies.
In Mann’s case, doctors at Fortis Hospital in Mohali confirmed his diagnosis after he presented with symptoms of tropical fever. Blood tests revealed the presence of Leptospira bacteria, prompting doctors to begin targeted antibiotic therapy. Although leptospirosis can have serious consequences if left untreated, timely medical intervention can effectively manage the condition, as seen in the Chief Minister’s case. According to his doctors, Mann’s vital signs were stable, and he was responding positively to treatment.
Riya Barde or better Known as aliases Arohi Barde and Banna Sheikh—Aressted In Mumbai, India
Symptoms of Leptospirosis
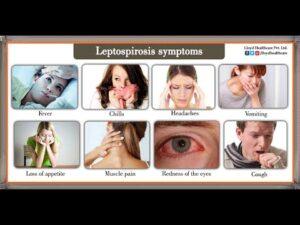
The symptoms of leptospirosis can vary widely, ranging from mild flu-like symptoms to more severe manifestations. The disease typically presents in two phases:
- The Leptospiremic Phase: This is the initial phase of the infection, where patients may experience non-specific symptoms such as fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, vomiting, and red eyes. In some cases, patients may also experience jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) if the liver is affected. During this phase, the bacteria multiply in the bloodstream and may cause systemic inflammation.
- The Immune Phase: The second phase occurs when the body’s immune system begins to respond to the infection. This phase can lead to more serious complications, including meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord), kidney damage, liver failure, and respiratory distress. In severe cases, leptospirosis can lead to a life-threatening condition known as Weil’s disease, characterized by multi-organ failure and internal bleeding.
In Bhagwant Mann’s case, his initial symptoms included pulmonary artery pressure, which prompted medical tests to diagnose the underlying cause. Pulmonary artery pressure can be a serious complication of leptospirosis if left untreated, as the infection can spread to various organs, including the heart and lungs.
Treatment and Recovery
The treatment for leptospirosis typically involves the use of antibiotics such as penicillin, doxycycline, or azithromycin, depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to preventing complications. In Mann’s case, doctors acted quickly to identify the infection and initiate appropriate treatment. Dr. RK Jaswal, Director and Head of Cardiology at Fortis Hospital, confirmed that Mann’s clinical parameters had improved significantly following treatment, indicating a positive response to the antibiotics.
In addition to antibiotics, supportive care may be required for patients with severe symptoms. This could include hydration, management of electrolyte imbalances, and, in extreme cases, intensive care for organ support. In Mann’s case, his vital signs were closely monitored to ensure that his recovery remained on track.
Samsung Galaxy S26 Tipped for Major Gains— A Glimpse Into the Future of Smartphones
Public Health Implications

The diagnosis of leptospirosis in a high-profile figure like Punjab’s Chief Minister has brought the disease into the public spotlight. Leptospirosis is often underreported in many regions due to a lack of awareness and diagnostic capabilities. However, outbreaks are not uncommon, particularly in areas with poor sanitation, flooding, and a high prevalence of animals that serve as carriers of the bacteria.
Public health authorities emphasize the importance of preventive measures to reduce the risk of leptospirosis transmission. These measures include:
- Avoiding contact with contaminated water: People living in or visiting areas prone to leptospirosis should avoid swimming or wading in water that may be contaminated with animal urine.
- Wearing protective clothing: Individuals who work in environments where they may come into contact with contaminated water or soil, such as farmers and agricultural workers, should wear protective gear, including gloves, boots, and long-sleeved clothing.
- Vaccination of animals: Vaccinating livestock and pets, especially dogs, can help reduce the risk of transmission to humans. Proper waste disposal and rodent control are also important in preventing the spread of the bacteria.
- Proper sanitation: Ensuring clean water supplies, proper waste management, and controlling rodent populations can help mitigate the risk of leptospirosis outbreaks in vulnerable communities.
The Role of Climate and Environment
Leptospirosis is closely linked to environmental factors, particularly in regions with heavy rainfall and flooding. The bacteria thrive in warm, wet conditions, making certain parts of India, including Punjab, susceptible to outbreaks. Flooding can disperse animal waste, contaminating water sources and increasing the likelihood of human exposure to Leptospira bacteria.
Climate change may also contribute to the spread of leptospirosis, as changes in weather patterns lead to more frequent and severe flooding in certain regions. Public health experts stress the need for climate resilience in health systems, particularly in managing waterborne diseases like leptospirosis. As extreme weather events become more common, proactive measures, such as flood management and community health education, are critical in preventing outbreaks.
Our Final Conclusion
Punjab CM Bhagwant Mann’s diagnosis with leptospirosis has drawn attention to this serious bacterial infection that is often overlooked. While it can lead to severe health complications, early diagnosis and treatment, as seen in Mann’s case, significantly improve outcomes. His swift recovery underlines the importance of timely medical intervention, but also serves as a reminder of the environmental and public health factors that contribute to the spread of zoonotic diseases like leptospirosis.
With climate change potentially exacerbating the conditions that facilitate the spread of leptospirosis, it is crucial for public health systems to prioritize prevention and preparedness. Efforts such as community education, sanitation improvements, and environmental management will be key to reducing the risk of future outbreaks. For now, Mann’s recovery offers a positive example of how prompt action can lead to successful outcomes, even in the face of potentially dangerous infections. Also follow us on Instagram & Facebook for more info about other things.
